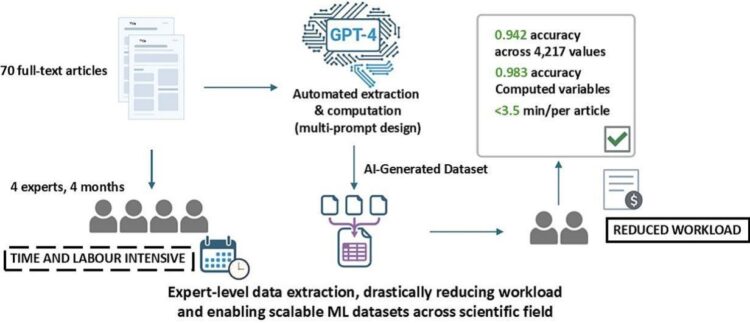
Creating high-quality datasets for training machine learning models in specialized domains like pharmaceutical research is often constrained by the manual effort required to extract and compute critical parameters from heterogeneous literature. A novel deep prompt-engineering framework was developed to transform GPT-4 into a robust tool for automated and accelerated generation of structured datasets. Using a multi-set prompt strategy, GPT-4 analysed 70 full-text articles from literature on pharmaceutical inkjet printing to extract and compute 22 domain-relevant variables. These variables were organized into three main parameter groups: (i) printing parameters, (ii) rheological properties, and (iii) drug dose parameters, which were analysed using dedicated prompts. The outputs were benchmarked against a human-curated dataset compiled over four months by four domain experts, previously used to train machine learning models for predicting inkjet printability.
+33 2 32 80 88 00
Contact